4 min read
Auth Series #4 - Call ASP.NET Core API Protected By Azure AD/Microsoft Entra ID via Console App Using Device Code Flow
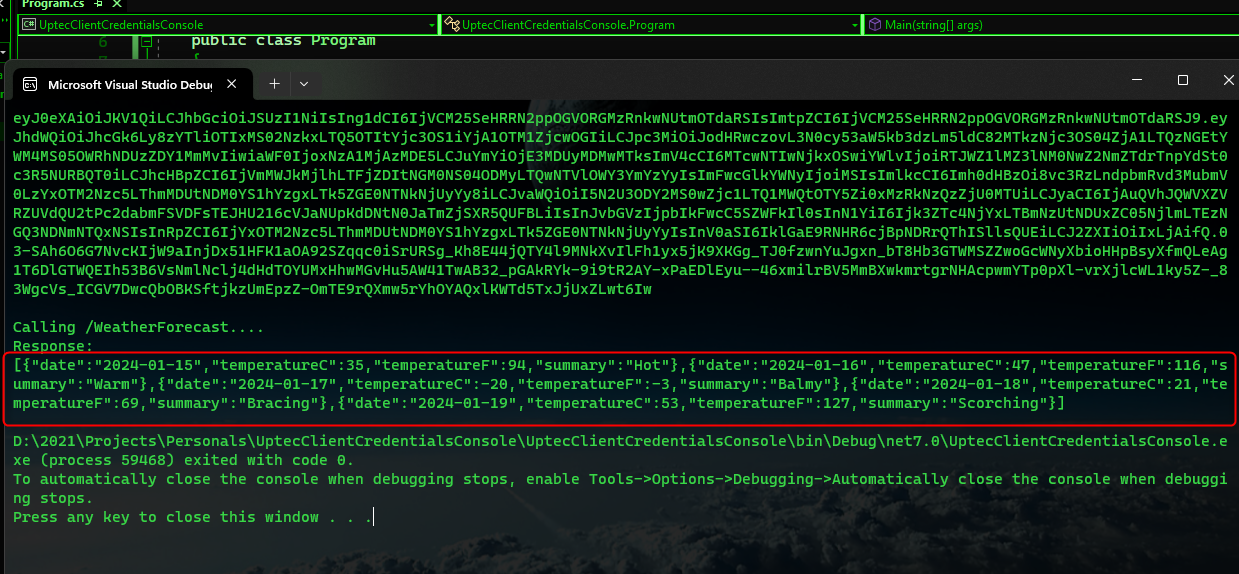
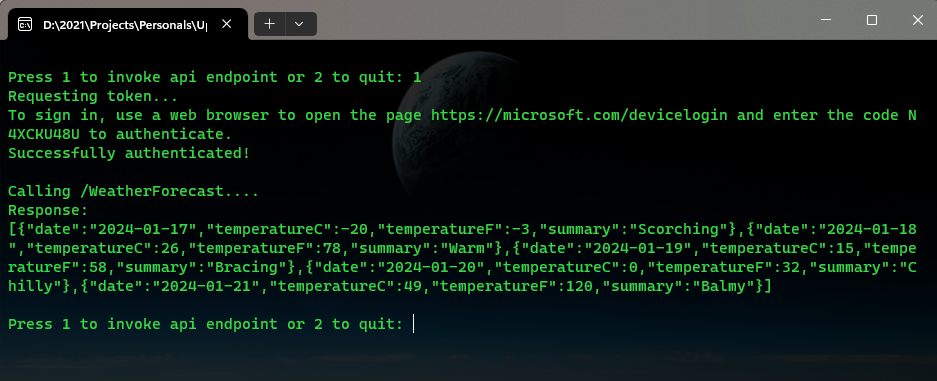
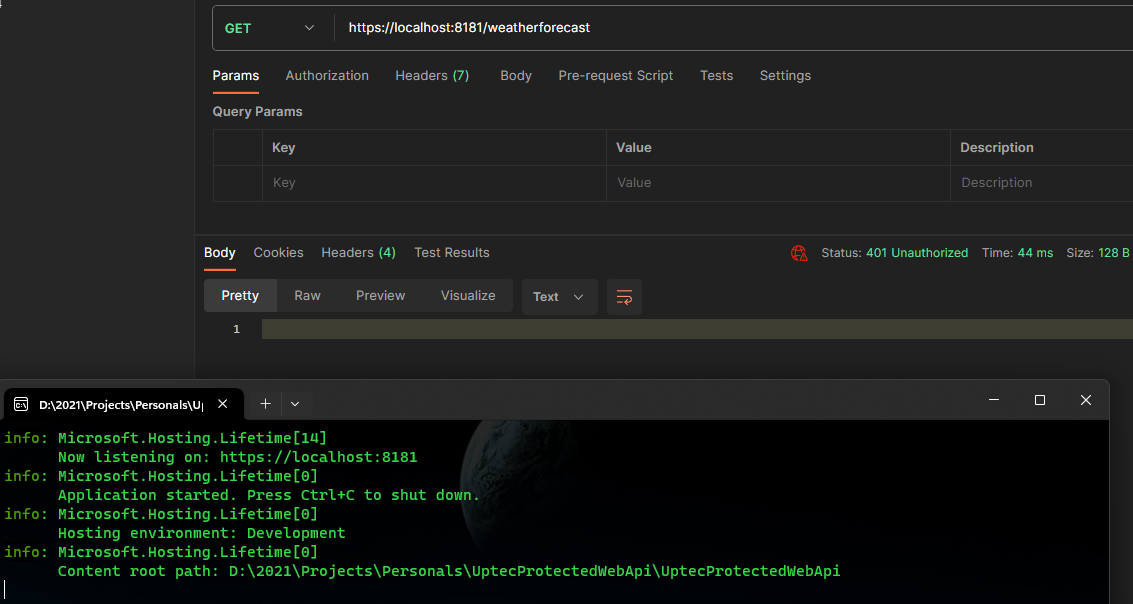
Auth Series #4 - Call ASP.NET Core API Protected By Azure AD/Microsoft Entra ID via Console App Using Device Code Flow This is the 4th tutorial of...